Taxonomic group: bacteria / Fusobacteria
(Phylum: Fusobacteria)
Host organism: Homo sapiens
Associated disease: periodontitis [ICD11:
DA0C 
];
infection due to Fusobacterium nucleatum [ICD11:
XN4P8 
]
The structure was elucidated in this paperNCBI PubMed ID: 28135570Publication DOI: 10.1016/j.carres.2017.01.002Journal NLM ID: 0043535Publisher: Elsevier
Correspondence: Evgeny.Vinogradov

nrc-cnrc.gc.ca
Institutions: Vaccine Program, Human Health Therapeutics Portfolio, National Research Council, Ottawa, ON K1A 0R6, Canada
Fusobacterium nucleatum is an anaerobic bacterium found in the human mouth where it causes periodontitis. Recently, it has been gaining attention as a potential causative agent for colorectal cancer and is strongly linked with pregnancy complications including pre-term and still births. Little is known about the virulence factors of this organism, and thus we have initiated studies to examine the bacterium's surface glycochemistry. We isolated lipopolysaccharide (LPS) from F. nucleatum strain 25586 and purified and performed structural analysis on the O-antigen polysaccharide. The polysaccharide contained two novel sugars, 2-acetamido-2,6-dideoxy-l-altrose (l-6dAltNAc) and a 5-acetimidoylamino-3,5,9-trideoxy-gluco-non-2-ulosonic acid (Non5Am), which was tentatively assigned the l-glycero-l-gluco configuration. The polysaccharide was found to have a trisaccharide repeating unit, which is phosphorylated with phosphocholine (PCho), and the following structure was established: -[-4-β-Nonp5Am-4-α-l-6dAltpNAc3PCho-3-β-d-QuipNAc-]- We propose the trivial name 'fusaminic acid' for the novel nonulosonic acid. It is the first occurrence of a 9-deoxynonulosonic acid with a hydroxyl group at C-7, which is occupied by an amino group in all monosaccharides of this class described so far.
Lipopolysaccharide, NMR, structure, Fusobacterium, Fusobacterium nucleatum, Fusaminic acid
Structure type: monomer
Location inside paper: table 1, p.13, PS
Aglycon: (1->4) O-antigen (ID 11979)
Compound class: O-polysaccharide, O-antigen
Methods: 13C NMR, 1H NMR, GLC-MS, GC-MS, de-O-acylation, sugar analysis, acid hydrolysis, anion-exchange chromatography, HPLC, GPC, HF treatment, acetylation
Comments, role: The non-reducing end of PS. Determination of C8 in Sug as L-glycero is speculative.
Related record ID(s): 11979, 12262, 12263, 12264
NCBI Taxonomy refs (TaxIDs): 851
Show glycosyltransferases
NMR conditions: in D2O at 308 K
[as TSV]
13C NMR data:
Linkage Residue C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 C9
4 Ac ? 21.06-22.0
5 Am 167.7 19.5
bXFusp ? ? 33.0 68.4 49.0 70.6 72.0 67.5 18.0
1H NMR data:
Linkage Residue H1 H2 H3 H4 H5 H6 H7 H8 H9
4 Ac - 2.07-2.10
5 Am ? 2.36
bXFusp - - 2.05-2.74 5.08 3.90 3.93-4.03 3.53 3.86 1.18
1H/13C HSQC data:
Linkage Residue C1/H1 C2/H2 C3/H3 C4/H4 C5/H5 C6/H6 C7/H7 C8/H8 C9/H9
4 Ac 21.06-22.0/2.07-2.10
5 Am 167.7/? 19.5/2.36
bXFusp 33.0/2.05-2.74 68.4/5.08 49.0/3.90 70.6/3.93-4.03 72.0/3.53 67.5/3.86 18.0/1.18
1H NMR data:
| Linkage | Residue | H1 | H2 | H3 | H4 | H5 | H6 | H7 | H8 | H9 |
|---|
| 4 | Ac |
| 2.07
2.10 | |
| 5 | Am | ? | 2.36 | |
| | bXFusp |
|
| 2.05
2.74 | 5.08 | 3.90 | 3.93
4.03 | 3.53 | 3.86 | 1.18 |
|
13C NMR data:
| Linkage | Residue | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | C9 |
|---|
| 4 | Ac | ? | 21.06
22.0 | |
| 5 | Am | 167.7 | 19.5 | |
| | bXFusp | ? | ? | 33.0 | 68.4 | 49.0 | 70.6 | 72.0 | 67.5 | 18.0 |
|
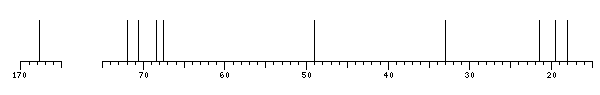
The spectrum also has 3 signals at unknown positions (not plotted). |
There is only one chemically distinct structure:
 report error
report error report error
report error