 Found 4 records.
Displayed records from 1 to 4
Found 4 records.
Displayed records from 1 to 4
Expand all records
Collapse all records
Show all as text (SweetDB notation)
Show all graphically (SNFG notation)
Shi T, Qi J, Shao CL, Zhao DL, Hou XM, Wang CY
Bioactive diphenyl ethers and isocoumarin derivatives from a gorgonian-derived fungus Phoma sp. (TA07-1)
Marine Drugs 15(6) (2017)
e146
|
b-D-Glcp-(1-2)-Subst
Subst = 4-(3-hydroxy-5-methylphenoxy)-5-methylbenzene-1,3-diol = SMILES O{53}C1=CC(C)=C(OC2=C{2}C(O)=CC(C)=C2){4}C(O)=C1 |
Show graphically |
Phoma sp. TA07-1

(Ancestor NCBI TaxID 37463,
species name lookup)
Taxonomic group: fungi / Ascomycota
(Phylum: Ascomycota)
Host organism: Dichotella gemmacea GX-WZ-2008003-4
The structure was elucidated in this paperNCBI PubMed ID: 28587090Publication DOI: 10.3390/md15060146Journal NLM ID: 101213729Publisher: Basel, Switzerland: Molecular Diversity Preservation International
Correspondence: changyun

ouc.edu.cn
Institutions: Key Laboratory of Marine Drugs, School of Medicine and Pharmacy, Ocean University of China, the Ministry of Education of China, Qingdao, China, Laboratory for Marine Drugs and Bioproducts, Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology, Qingdao, China, Institute of Evolution & Marine Biodiversity, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China
Three new diphenyl ether derivatives-phomaethers A-C (1-3) and five known compounds-including a diphenyl ether analog, 2,3'-dihydroxy-4-methoxy-5',6-dimethyl diphenyl ether (4); and four isocoumarin derivatives, diaportinol (5), desmethyldiaportinol (6), citreoisocoumarinol (7), and citreoisocoumarin (8)-were isolated from a gorgonian-derived fungus Phoma sp. (TA07-1). Their structures were elucidated by extensive spectroscopic investigation. The absolute configurations of 1 and 2 were determined by acid hydrolysis reactions. It was the first report to discover the diphenyl glycoside derivatives from coral-derived fungi. Compounds 1, 3, and 4 showed selective strong antibacterial activity against five pathogenic bacteria with the minimum inhibiting concentration (MIC) values and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) values between 0.156 and 10.0 μM.
antibacterial activity, diphenyl ether, Phoma sp., gorgonian-derived fungus, isocoumarin
Structure type: monomer ; 445.1474 [M+Na]+
C
21H
26O
9Location inside paper: compound 1, Figure 1(1), Table 1(1), Phomaether A
Trivial name: diphenyl ether glycoside
Contained glycoepitopes: IEDB_142488,IEDB_146664,IEDB_983931,SB_192
Methods: 13C NMR, 1H NMR, IR, HPLC, UV, HMBC, HMQC, COSY, HRESIMS, ESIMS, VLC
Biological activity: compound 1 exhibited remarkable antibacterial activity against S. albus, S. aureus, E. coli, and V. parahaemolyticus with MIC values ranging from 0.312 to 0.625 µM and MBC values from 0.625 to 2.50 µM and demonstrated moderate lethality to the brine shrimp A. salina with the LC50 values ranging from 14.01 ± 0.36 to 37.33 ± 0.26 µg/mL
Related record ID(s): 43265
NCBI Taxonomy refs (TaxIDs): 37463
Show glycosyltransferases
NMR conditions: in DMSO-d6
[as TSV]
13C NMR data:
Linkage Residue C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 C9 C10 C11 C12 C13 C14 C15 C16 C17
2 bDGlcp 100.76 73.2 76.8 69.8 77.3 60.8
Subst 135.2 150.9 100.82 156.3 108.5 132.4 55.2 55.2 16.2 159.3 99.2 158.2 109.4 139.5 106.6 - 21.2
1H NMR data:
Linkage Residue H1 H2 H3 H4 H5 H6 H7 H8 H9 H10 H11 H12 H13 H14 H15 H16 H17
2 bDGlcp 4.82 3.06 3.20 3.08 3.30 3.40-3.68
Subst - - 6.69 - 6.51 - 3.73 3.73 2.02 - 5.93 - 9.27 2.13 6.18 - 6.08
1H/13C HSQC data:
Linkage Residue C1/H1 C2/H2 C3/H3 C4/H4 C5/H5 C6/H6 C7/H7 C8/H8 C9/H9 C10/H10 C11/H11 C12/H12 C13/H13 C14/H14 C15/H15 C16/H16 C17/H17
2 bDGlcp 100.76/4.82 73.2/3.06 76.8/3.20 69.8/3.08 77.3/3.30 60.8/3.40-3.68
Subst 100.82/6.69 108.5/6.51 55.2/3.73 55.2/3.73 16.2/2.02 99.2/5.93 109.4/9.27 139.5/2.13 106.6/6.18 21.2/6.08
1H NMR data:
| Linkage | Residue | H1 | H2 | H3 | H4 | H5 | H6 | H7 | H8 | H9 | H10 | H11 | H12 | H13 | H14 | H15 | H16 | H17 |
|---|
| 2 | bDGlcp | 4.82 | 3.06 | 3.20 | 3.08 | 3.30 | 3.40
3.68 | |
| | Subst |
|
| 6.69 |
| 6.51 |
| 3.73 | 3.73 | 2.02 |
| 5.93 |
| 9.27 | 2.13 | 6.18 |
| 6.08 |
|
13C NMR data:
| Linkage | Residue | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | C9 | C10 | C11 | C12 | C13 | C14 | C15 | C16 | C17 |
|---|
| 2 | bDGlcp | 100.76 | 73.2 | 76.8 | 69.8 | 77.3 | 60.8 | |
| | Subst | 135.2 | 150.9 | 100.82 | 156.3 | 108.5 | 132.4 | 55.2 | 55.2 | 16.2 | 159.3 | 99.2 | 158.2 | 109.4 | 139.5 | 106.6 |
| 21.2 |
|

The spectrum also has 1 signal at unknown position (not plotted). |
There is only one chemically distinct structure:
Expand this record
Collapse this record
Shi T, Qi J, Shao CL, Zhao DL, Hou XM, Wang CY
Bioactive diphenyl ethers and isocoumarin derivatives from a gorgonian-derived fungus Phoma sp. (TA07-1)
Marine Drugs 15(6) (2017)
e146
|
a-D-Ribf-(1-3')-Subst
Subst = 4-(3-hydroxy-5-methylphenoxy)-5-methylbenzene-1,3-diol = SMILES O{53}C1=CC(C)=C(OC2=C{2}C(O)=CC(C)=C2){4}C(O)=C1 |
Show graphically |
Phoma sp. TA07-1

(Ancestor NCBI TaxID 37463,
species name lookup)
Taxonomic group: fungi / Ascomycota
(Phylum: Ascomycota)
Host organism: Dichotella gemmacea GX-WZ-2008003-4
The structure was elucidated in this paperNCBI PubMed ID: 28587090Publication DOI: 10.3390/md15060146Journal NLM ID: 101213729Publisher: Basel, Switzerland: Molecular Diversity Preservation International
Correspondence: changyun

ouc.edu.cn
Institutions: Key Laboratory of Marine Drugs, School of Medicine and Pharmacy, Ocean University of China, the Ministry of Education of China, Qingdao, China, Laboratory for Marine Drugs and Bioproducts, Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology, Qingdao, China, Institute of Evolution & Marine Biodiversity, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China
Three new diphenyl ether derivatives-phomaethers A-C (1-3) and five known compounds-including a diphenyl ether analog, 2,3'-dihydroxy-4-methoxy-5',6-dimethyl diphenyl ether (4); and four isocoumarin derivatives, diaportinol (5), desmethyldiaportinol (6), citreoisocoumarinol (7), and citreoisocoumarin (8)-were isolated from a gorgonian-derived fungus Phoma sp. (TA07-1). Their structures were elucidated by extensive spectroscopic investigation. The absolute configurations of 1 and 2 were determined by acid hydrolysis reactions. It was the first report to discover the diphenyl glycoside derivatives from coral-derived fungi. Compounds 1, 3, and 4 showed selective strong antibacterial activity against five pathogenic bacteria with the minimum inhibiting concentration (MIC) values and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) values between 0.156 and 10.0 μM.
antibacterial activity, diphenyl ether, Phoma sp., gorgonian-derived fungus, isocoumarin
Structure type: monomer ; 415.1370 [M+Na]+
C
20H
24O
8Location inside paper: compound 2, Figure 1(2), Table 1(2), Phomaether B
Compound class: diphenyl ether glycoside
Contained glycoepitopes: IEDB_149136
Methods: 13C NMR, 1H NMR, IR, HPLC, UV, HMBC, HMQC, COSY, HRESIMS, ESIMS, VLC
Related record ID(s): 43264
NCBI Taxonomy refs (TaxIDs): 37463
Show glycosyltransferases
NMR conditions: in CD3OD
[as TSV]
13C NMR data:
Linkage Residue C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 C9 C10 C11 C12 C13 C14 C15 C16 C17 C18
3' aDRibf 102.3 73.4 71.2 87.5 63.2
Subst 135.6 151.8 101.4 158.7 107.8 134.0 55.2 55.8 16.5 160.7 102.6 159.8 111.7 141.3 110.4 - 21.8 110.4
1H NMR data:
Linkage Residue H1 H2 H3 H4 H5 H6 H7 H8 H9 H10 H11 H12 H13 H14 H15 H16 H17 H18
3' aDRibf 5.55 4.13 4.06 4.10 3.63-3.69
Subst - - 6.35 - 6.31 - 3.74 3.74 2.03 - 6.39 - 9.27 2.24 6.60 - 6.08 6.29
1H/13C HSQC data:
Linkage Residue C1/H1 C2/H2 C3/H3 C4/H4 C5/H5 C6/H6 C7/H7 C8/H8 C9/H9 C10/H10 C11/H11 C12/H12 C13/H13 C14/H14 C15/H15 C16/H16 C17/H17 C18/H18
3' aDRibf 102.3/5.55 73.4/4.13 71.2/4.06 87.5/4.10 63.2/3.63-3.69
Subst 101.4/6.35 107.8/6.31 55.2/3.74 55.8/3.74 16.5/2.03 102.6/6.39 111.7/9.27 141.3/2.24 110.4/6.60 21.8/6.08 110.4/6.29
1H NMR data:
| Linkage | Residue | H1 | H2 | H3 | H4 | H5 | H6 | H7 | H8 | H9 | H10 | H11 | H12 | H13 | H14 | H15 | H16 | H17 | H18 |
|---|
| 3' | aDRibf | 5.55 | 4.13 | 4.06 | 4.10 | 3.63
3.69 | |
| | Subst |
|
| 6.35 |
| 6.31 |
| 3.74 | 3.74 | 2.03 |
| 6.39 |
| 9.27 | 2.24 | 6.60 |
| 6.08 | 6.29 |
|
13C NMR data:
| Linkage | Residue | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | C9 | C10 | C11 | C12 | C13 | C14 | C15 | C16 | C17 | C18 |
|---|
| 3' | aDRibf | 102.3 | 73.4 | 71.2 | 87.5 | 63.2 | |
| | Subst | 135.6 | 151.8 | 101.4 | 158.7 | 107.8 | 134.0 | 55.2 | 55.8 | 16.5 | 160.7 | 102.6 | 159.8 | 111.7 | 141.3 | 110.4 |
| 21.8 | 110.4 |
|

The spectrum also has 1 signal at unknown position (not plotted). |
There is only one chemically distinct structure:
Expand this record
Collapse this record
Fan HX, Zhou ZQ, Peng J, Wu BJ, Chen HR, Bao XF, Mu ZQ, Jiao WH, Yao XS, Gao H
A microbial model of mammalian metabolism: biotransformation of 4,5-dimethoxyl-canthin-6-one using Cunninghamella blakesleeana CGMCC 3.970
Xenobiotica 47(4) (2017)
284-289
|
b-D-Glcp-(1-15)-Subst
Subst = nigakinone = SMILES COC1={15}C(C(N2C3=CC=CC=C3C4=C2C1=NC=C4)=O)O |
Show graphically |
Cunninghamella blakesleeana CGMCC 3.970

(Ancestor NCBI TaxID 155726,
species name lookup)
Taxonomic group: fungi / Mucoromycota
(Phylum: Mucoromycota)
The structure was elucidated in this paperNCBI PubMed ID: 27237303Publication DOI: 10.1080/00498254.2016.1184774Journal NLM ID: 1306665Publisher: London: Informa Healthcare
Correspondence: Gao H <tghao

jnu.edu.cn>
Institutions: Institute of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Natural Products, College of Pharmacy, Jinan University, Guangzhou, China, Division of Pharmaceutics, College of Pharmacy, Jinan University, Guangzhou, China, College of Traditional Chinese Materia Medica, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, Shenyang, China
A filamentous fungus, Cunninghamella blakesleeana CGMCC 3.970, was applied as a microbial system to mimic mammalian metabolism of 4,5-dimethoxyl-canthin-6-one (1). Compound 1 belongs to canthin-6-one type alkaloids, which is a major bioactive constituent of a traditional Chinese medicine (the stems of Picrasma quassioides). 2. After 72 h of incubation in potato dextrose broth, 1 was metabolized to seven metabolites as follows: 4-methoxyl-5-hydroxyl-canthin-6-one (M1), 4-hydroxyl-5-methoxyl-canthin-6-one (M2), canthin-6-one (M3), canthin-6-one N-oxide (M4), 10-hydroxyl-4,5-dimethoxyl-canthin-6-one (M5), 1-methoxycarbonl-β-carboline (M6), and 4-methoxyl-5-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-canthin-6-one (M7). 3. The structures of metabolites were determined using spectroscopic analyses, chemical methods, and comparison of NMR data with those of known compounds. Among them, M7 was a new compound. 4. The metabolic pathways of 1 were proposed, and the metabolic processes involved phase I (O-demethylation, dehydroxylation, demethoxylation, N-oxidation, hydroxylation, and oxidative ring cleavage) and phase II (glycosylation) reactions. 5. This was the first research on microbial transformation of canthin-6-one alkaloid, which could be a useful microbial model for producing the mammalian phase I and phase II metabolites of canthin-6-one alkaloids. 6. 1, M1-M5, and M7 are canthin-6-one alkaloids, whereas M6 belongs to β-carboline type alkaloids. The strain of Cunninghamella blakesleeana can supply an approach to transform canthin-6-one type alkaloids into β-carboline type alkaloids.
4, microbial transformation, Cunninghamella blakesleeana, 5-dimethoxyl-canthin-6-one, canthin-6-one alkaloids, microbial model of mammalian metabolism
Structure type: monomer ; 429.1303 [M+H]+
C
21H
21N
2O
8Location inside paper: Figure 1(M7), M7, Figure 2
Compound class: glycoside
Contained glycoepitopes: IEDB_142488,IEDB_146664,IEDB_983931,SB_192
Methods: 13C NMR, 1H NMR, IR, acid hydrolysis, HPLC, UV, ROESY, COSY, HSQC, HRESIMS, ESIMS, HMDC
Synthetic data: biosynthesis
NCBI Taxonomy refs (TaxIDs): 155726
Show glycosyltransferases
NMR conditions: in DMSO-d6
[as TSV]
13C NMR data:
Linkage Residue C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 C9 C10 C11 C12 C13 C14 C15 C16 C17
15 bDGlcp 101.7 74.2 76.5 69.9 77.6 60.9
Subst - 128.1 133.0 - 145.2 116.5 129.3 124.5 123.5 125.5 130.8 116.1 138.3 153.6 136.5 157.5 61.7
1H NMR data:
Linkage Residue H1 H2 H3 H4 H5 H6 H7 H8 H9 H10 H11 H12 H13 H14 H15 H16 H17
15 bDGlcp 5.32 3.34 3.32 3.18 3.16 3.44-3.65
Subst - - - - 8.81 8.23 - - 8.30 7.54 7.72 8.44 - - - - 4.38
1H/13C HSQC data:
Linkage Residue C1/H1 C2/H2 C3/H3 C4/H4 C5/H5 C6/H6 C7/H7 C8/H8 C9/H9 C10/H10 C11/H11 C12/H12 C13/H13 C14/H14 C15/H15 C16/H16 C17/H17
15 bDGlcp 101.7/5.32 74.2/3.34 76.5/3.32 69.9/3.18 77.6/3.16 60.9/3.44-3.65
Subst 145.2/8.81 116.5/8.23 123.5/8.30 125.5/7.54 130.8/7.72 116.1/8.44 61.7/4.38
1H NMR data:
| Linkage | Residue | H1 | H2 | H3 | H4 | H5 | H6 | H7 | H8 | H9 | H10 | H11 | H12 | H13 | H14 | H15 | H16 | H17 |
|---|
| 15 | bDGlcp | 5.32 | 3.34 | 3.32 | 3.18 | 3.16 | 3.44
3.65 | |
| | Subst |
|
|
|
| 8.81 | 8.23 |
|
| 8.30 | 7.54 | 7.72 | 8.44 |
|
|
|
| 4.38 |
|
13C NMR data:
| Linkage | Residue | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | C9 | C10 | C11 | C12 | C13 | C14 | C15 | C16 | C17 |
|---|
| 15 | bDGlcp | 101.7 | 74.2 | 76.5 | 69.9 | 77.6 | 60.9 | |
| | Subst |
| 128.1 | 133.0 |
| 145.2 | 116.5 | 129.3 | 124.5 | 123.5 | 125.5 | 130.8 | 116.1 | 138.3 | 153.6 | 136.5 | 157.5 | 61.7 |
|
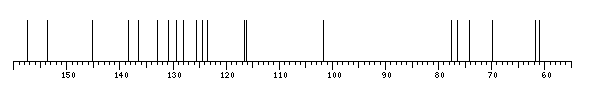
The spectrum also has 2 signals at unknown positions (not plotted). |
There is only one chemically distinct structure:
Expand this record
Collapse this record
Harms H, Rempel V, Kehraus S, Kaiser M, Hufendiek P, Müller CE, Konig GM
Indoloditerpenes from a marine-derived fungal strain of Dichotomomyces cejpii with antagonistic activity at GPR18 and cannabinoid receptors
Journal of Natural Products 77(3) (2014)
673-677
|
b-D-Manp-(1-7)-Subst
Subst = indoloditerpene = SMILES [H][C@]1(C2)[C@]([C@](CC{7}[C@H](O)[C@]3(CC/C=C(C)\C)C)(C)[C@@]3([H])CC1)(C)C4=C2C5=CC=CC=C5N4 |
Show graphically |
Dichotomomyces cejpii
 (previously named: Talaromyces cejpii; later renamed to: Aspergillus cejpii)
(previously named: Talaromyces cejpii; later renamed to: Aspergillus cejpii)
(NCBI TaxID 1884262,
species name lookup)
Taxonomic group: fungi / Ascomycota
(Phylum: Ascomycota)
Host organism: Callyspongia
The structure was elucidated in this paperNCBI PubMed ID: 24471526Publication DOI: 10.1021/np400850gJournal NLM ID: 7906882Publisher: American Society of Pharmacognosy
Correspondence: Müller CE <christa.mueller

uni-bonn.de>; König GM <g.koenig

uni-bonn.de>
Institutions: Institute for Pharmaceutical Biology, University of Bonn, Bonn, Germany, Pharma Center Bonn, Pharmaceutical Institute, Pharmaceutical Chemistry I, University of Bonn, Bonn, Germany, Swiss Tropical and Public Health Institute, Basel, Switzerland, University of Basel, Basel, Switzerland
A marine-derived strain of Dichotomomyces cejpii produces the new compounds emindole SB beta-mannoside (1) and 27-O-methylasporyzin C (2), as well as the known indoloditerpenes JBIR-03 (3) and emindole SB (4). Indole derivative 1 was found to be a CB2 antagonist, while 2 was identified as the first selective GPR18 antagonist with an indole structure. Compound 4 was found to be a nonselective CB1/CB2 antagonist. The new natural indole derivatives may serve as lead structures for the development of GPR18- and CB receptor-blocking drugs.
Dichotomomyces cejpii, indoloditerpene, antagonistic activity, emindole SB beta-mannoside
Structure type: monomer ; 590.3440 [M+Na]+
C
34H
49NO
6Location inside paper: emindole SB beta-mannoside, compound 1, Chart 1(1), Table 1(1)
Compound class: glycoside
Contained glycoepitopes: IEDB_137485,IEDB_144983,IEDB_152206,IEDB_983930,SB_44,SB_72
Methods: 13C NMR, 1H NMR, IR, HPLC, UV, optical rotation measurement, binding assays, cytotoxicity assay, HMBC, COSY, NOESY, HSQC, DEPT-135, HRESIMS, HCl hydrolysis, ESIMS, VLC, cAMP phosphodiesterase assay
Biological activity: Compound 1 is a CB (cannabioid) receptor antagonist with a preference for the CB2 receptor subtype with a Ki value of 10.6 μM. Compound 1 showed no cytotoxic activity toward an L6 rat skeletal muscle cell line (IC50 58 μM).
Comments, role: NMR temperature was not specified
NCBI Taxonomy refs (TaxIDs): 1884262
Show glycosyltransferases
NMR conditions: in (CD3)2CO
[as TSV]
13C NMR data:
Linkage Residue C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 C7 C8 C9 C10 C11 C12 C13 C14 C15 C16 C17 C18 C19 C20 C21 C22 C23 C24 C25 C26 C27 C28
7 bDManp 103.5 72.2 75.5 69.2 77.6 63.2
Subst 152.0 53.8 39.7 33.3 26.8 83.9 42.0 40.7 23.3 25.9 49.7 28.0 117.7 126.0 118.6 119.6 120.5 112.5 141.5 15.0 19.4 17.9 38.2 22.2 125.8 131.1 25.9 17.8
1H NMR data:
Linkage Residue H1 H2 H3 H4 H5 H6 H7 H8 H9 H10 H11 H12 H13 H14 H15 H16 H17 H18 H19 H20 H21 H22 H23 H24 H25
7 bDManp 4.63 3.89 3.42 3.64 3.25 3.69-3.82
Subst - - - 1.81 1.45-1.63 1.65-1.75 2.75 2.29-2.62 - - 7.31 6.92 6.69 7.28 - 1.03 1.11 0.83 1.27-1.50 1.93-2.03 5.13 - 1.66 1.64 -
1H/13C HSQC data:
Linkage Residue C1/H1 C2/H2 C3/H3 C4/H4 C5/H5 C6/H6 C7/H7 C8/H8 C9/H9 C10/H10 C11/H11 C12/H12 C13/H13 C14/H14 C15/H15 C16/H16 C17/H17 C18/H18 C19/H19 C20/H20 C21/H21 C22/H22 C23/H23 C24/H24 C25/H25
7 bDManp 103.5/4.63 72.2/3.89 75.5/3.42 69.2/3.64 77.6/3.25 63.2/3.69-3.82
Subst NMR TSV error 2: unequal length of 13C and 1H datasets
1H NMR data:
| Linkage | Residue | H1 | H2 | H3 | H4 | H5 | H6 | H7 | H8 | H9 | H10 | H11 | H12 | H13 | H14 | H15 | H16 | H17 | H18 | H19 | H20 | H21 | H22 | H23 | H24 | H25 |
|---|
| 7 | bDManp | 4.63 | 3.89 | 3.42 | 3.64 | 3.25 | 3.69
3.82 | |
| | Subst |
|
|
| 1.81 | 1.45
1.63 | 1.65
1.75 | 2.75 | 2.29
2.62 |
|
| 7.31 | 6.92 | 6.69 | 7.28 |
| 1.03 | 1.11 | 0.83 | 1.27
1.50 | 1.93
2.03 | 5.13 |
| 1.66 | 1.64 |
|
|
13C NMR data:
| Linkage | Residue | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | C6 | C7 | C8 | C9 | C10 | C11 | C12 | C13 | C14 | C15 | C16 | C17 | C18 | C19 | C20 | C21 | C22 | C23 | C24 | C25 | C26 | C27 | C28 |
|---|
| 7 | bDManp | 103.5 | 72.2 | 75.5 | 69.2 | 77.6 | 63.2 | |
| | Subst | 152.0 | 53.8 | 39.7 | 33.3 | 26.8 | 83.9 | 42.0 | 40.7 | 23.3 | 25.9 | 49.7 | 28.0 | 117.7 | 126.0 | 118.6 | 119.6 | 120.5 | 112.5 | 141.5 | 15.0 | 19.4 | 17.9 | 38.2 | 22.2 | 125.8 | 131.1 | 25.9 | 17.8 |
|
There is only one chemically distinct structure:
Expand this record
Collapse this record
Total list of record IDs on all result pages of the current query:
Execution: 9 sec
 report error
report error Found 4 records.
Displayed records from 1 to 4
Found 4 records.
Displayed records from 1 to 4
 report error
report error
 ouc.edu.cn
ouc.edu.cn report error
report error
 ouc.edu.cn
ouc.edu.cn report error
report error
 jnu.edu.cn>
jnu.edu.cn> report error
report error (previously named: Talaromyces cejpii; later renamed to: Aspergillus cejpii)
(previously named: Talaromyces cejpii; later renamed to: Aspergillus cejpii) uni-bonn.de>; König GM <g.koenig
uni-bonn.de>; König GM <g.koenig uni-bonn.de>
uni-bonn.de>